Practice Mensuration - quantitative aptitude Online Quiz (set-2) For All Competitive Exams
Q-1) The dimensions of a field are 15 m by 12 m. A pit 8 m long, 2.5 m wide and 2 m deep is dug in one corner of the field and the earth removed is evenly spread over the remaining area of the field. The level of the field is raised by
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
![]()
Volume of pit = l b h = 8 × 2.5 × 2 = 40 $m^3$.
Let the label of the earth spread over remaining area = h.
Volume of the earth spread = Volume of a pit
⇒ [(12 × 15) – (8 × 2.5)] × h = 40
∴ h = ${40}/{180 - 20} = {40}/{160} = 1/4$m = 25 cm
Q-2) The length of a minute hand of a wall clock is 9 cm. What is the area swept (in $cm^2$) by the minute hand in 20 min? (take π = 3.14)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
The angle made by the minute hand in 20 min = 120°
∴ The area swept by the minute hand in 20 min
= $θ/{360°} × π r^2 = ∼ {120°}/{360°} × 3.14 × 9 × 9 = 84.78 cm^2$
Q-3) In a Δ ABC, AD is the median through A and E is the mid– point of AD and BE produced meets AC at F. Then, AF is equal to
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
In ΔABC, we draw a line l || BF which intersect AC at G. In ΔADG and ΔAEF;
given that EA is the mid point of AD and DL || EF.
So, concept of similar triangle.
F is also mid point of AG. AF = FG (i)
DADG and DAEF are similar.
Again
ΔFBC and ΔDCl
BF || DG
given that AD is median so thad DB the mid point of BC.
G will be The mid point of CF
CG = GF ...(ii)
From equations (i) and (ii), we get
AF = FG = CG ...(iii)
From figure, AC = AF = FG + CG
= AF + AF + AF + 3AF
⇒ AF = $1/3$ AC
Q-4) A cardboard sheet in the form of a circular sector of radius 30 cm and central angle 144º is folded to make a cone. What is the radius of the cone?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
length of the are = 2 π r $(θ/{360º})$
Radius of arc(r) = 30 am
Length of the arc = 2πr = 2π × 30 × ${144}/{360}$ = 24π
Let the radius of the cone = R ∴ 2πR = 24π
⇒ R = ${30 × 144}/{360}$ = 12cm
Q-5) A right circular cylinder just encloses a sphere. If p is the surface area of the sphere and q is the curved surface area of the cylinder, then which one of the following is correct?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
p = 4π$r^2$
q = 2πr.h = 2πr. 2r
= 4π $r^2$
Hence, P = q.
![]()
Q-6) 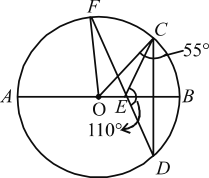
In the figure given above, AB is a diameter of the circle with centre O and EC = ED. What is ∠EFO?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
The Given,
![]()
⇒ ∠EDC = ∠ECD = 35°
Since, ∠OCD = 55°
Then, ∠OCE = 20°
By using then theorem that triangle on the same segment of a circle makes as equal angles.
Here, OE is a segment, which makes a ΔOFE and ΔOCE.
Therefore, ∠OCE = ∠EFO = 20°
Q-7) 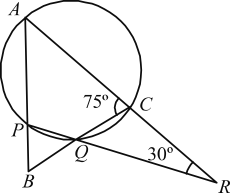
In the figure given above, what is ∠CBA?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
The sum of opposite angles in cyclic quadrilateral is always 180°.
∴ ∠ACQ + ∠APQ = 180°
75° + ∠APQ = 180°
∴ ∠APQ = 180° – 75° = 105°
∠ACQ + ∠QCR = 180° (∵ Straight line)
75° + ∠QCR = 180°
∠QCR = 180° – 75° = 105°
∠CQR = 180° – 105° – 30° = 45°
Since, ∠APQ + ∠BPQ = 180° (Straight line)
∴ 105° + ∠BPQ = 180°
∠BPQ = 75°
In ΔBPQ ∠B + ∠P + ∠Q = 180°
∠B + 75° + 45° = 180°
⇒ ∠B = 60° ∴ ∠CBA = 60°
Q-8) 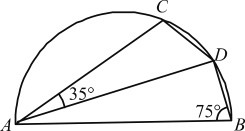
In the figure given above, C and D are points on the semi-circle described on AB as diameter. If ∠ABD = 75° and ∠DAC = 35°, then what is the ∠BDC?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Since, DADB is a right angled triangle at D.
![]()
∴ ∠DAB = 180° – (90° + 75°)
⇒ ∠DAB = 15°
Also, ABCD is cyclic quadrilateral.
∴ ∠CAB + ∠BDC = 180°
⇒ ∠BDC = 180° – (35° + 15°) = 130°
Q-9) PQ is a common chord of two circles. APB is a secant line joining points A and B on the two circles. Two tangents AC and BC are drawn. If ∠ACB = 45°, then what is ∠AQB equal to?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
The tangents drawn from an outer point on a circle are always equal = ∠CBA.
Therefore, ∠CAB = ∠CBA
![]()
∴ 45° + x + x = 180°
⇒ 2x = 180° – 45°
⇒ x = 67 ${1°}/2$
∠AQP = ∠x = ∠BQP
= 67 ${1°}/2$
(alternate interior segments properties)
⇒ ∠AQB = ∠AQP + ∠BQP
= $67 {1°}/2 + 67{1°}/2$ = 135°
Q-10) A circle of radius r is inscribed in a regular polygon with n sides (the circle touches all sides of the polygon). If the perimeter of the polygon is p, then the area of the polygon is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
The n-sided polygon can be dinded into 'n' triangle with O, the Centre of the circle as one vertex for each triangle. The altitude of each triangle is r. Let the sides of the polygon be '$a_1 ', a_2 ----- a_n$.(Given $a_1 = a_2 = ------ a_n$)
∴ The area of polygon is ${nr}/2 = {pr}/2$
Area of polygon = ${a_1r}/2 + {a_2r}/2 + --- {a_nr}/2 = {pr}/2$
So, option (a) is correct.
Q-11) 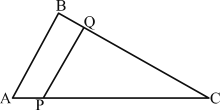
In the given triangle, AB is parallel to PQ. AP = c, PC = b, PQ = a, AB = x. What is the value of x?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
In ΔABC and ΔPQC,
![]()
∴ ${PC}/{AC} = {PQ}/{AB}$
⇒ $b/{c + a} = a/x$
∴ x = ${a(c + b)}/b = {ac}/b + a$
Q-12) If a square of side x and an equilateral triangle of side y are inscribed in a circle, then what is the ratio of x to y ?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Let Radius of circle be r
Case I (Square)
side = x
$x^2 + x^2 = (2r)^2$
![]()
$2x^2 = 4r^2$
x = $√2$r
Case II (equilateral triangle)
y cos30° = h
y × $√3/2$ = h
r = $2/3 × √3/2$ y
r = $y/√3$
[if h= 3 r = 2]
$y/{2r} = √3/2$
y = ${2 √3r}/2 = √3r$
$x/y = {√2 r}/{√3 r} = √{2/3}$
Q-13) Consider a circle C of radius 6 cm with centre at O. What is the difference in the area of the circle C and the area of the sector of C subtending an angle of 80º at O?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
![]()
Radius of circle, r = 6 cm
∴ Area of circle = $πr^2 = π × 6^2 = 36π cm^2$
and Area of sector subtending an angle of 80° at O
= ${π r^2 θ}/{360°} = {π × 6^2 × 80°}/{360°} = 8 π cm^2$
∴ Required difference = 36π – 8π = 28π $cm^2$
Q-14) The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 3$√10$ unit. If the smaller side is tripled and the longer side is doubled, new hypotenuse becomes 9$√5$ unit. What are the lengths of the smaller and longer sides of the right triangle, respectively?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Suppose the smaller and larger sides of a right triangle be x and y, respectively.
By given condition,
$x^2 + y^2 = (3 √{10})^2$
⇒ $x^2 + y^2$ = 90 ... (i)
and $9x^2 + 4y^2$ = 405 ... (ii)
On solving Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
x = 3 units and y = 9 units
Q-15) ABCD is a rectangle of dimensions 6 cm × 8 cm. DE and BF are the perpendiculars drawn on the diagonal of the rectangle. What is the ratio of the shaded to that of unshaded region?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
${\text"Area of Δ DAE "}/{\text"Area of Δ DEC"} = {1/2 × DE × AE}/{1/2 × DE × CE}$
= ${AE}/{CE} = {(AD)^2}/{(DC)^2} = (6/8)^2 = {9/{16}}$
Similarly, in ΔABC,
${\text"Area of ΔBCF"}/{\text"Area of ΔBFA"} = 9/{16}$
∴ The area of shaded to unshaded region = ${16}/9$
Q-16) ABCD is a quadrilateral such that BC = BA and CD > AD. Which one of the following is correct?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Construction : In quadrilateral ABCD, form A to C.
Now, in ΔABC
![]()
∵ AB = BC ...(Given)
∴ ∠BAC = ∠BCA
(angles opposite to equal side)
In ΔADC,
∵ CD > AD
∴ ∠DAC> ∠DCA
(since in a triangle, angle opposite to greater side is bigger than the angle opposite to smaller side)
On adding eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
∠BAD > ∠BCD
Q-17) A gardener increased the area of his rectangular garden by increasing its length by 40% and decreasing its width by 20%. The area of the new garden
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Let initial dimensions be, l & b
∴ Final length is 1.4 l
Final breadth is 0.8 b
∴ Final area is = 1.4 l × 0.8 b
= 1.12 lb
∴ Area is increased by 12%.
Shortcut Method : + 40 – 20 + ${40 × (-20)}/{100}$
= 20 – 8 = 12%
Therefore, the area of the new garden increased by 12%
Q-18) Which one of the following is a Pythagorean triple in which one side differs from the hypotenuse by two units?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
According to Pythagorean triplet.
The sum of square of base and perpendicular equal to square of hypotenuse.
By hit and trial method:—
$(2n)^2 + (n^2 – 1)^2 = (n^2 + 1)^2$
$4n^2 + n^4 + 1 – 2n^2 = n^4 + 2n^2$ + 1
$n^4 + 2n^2 + 1 = n^4 + 2n^2$ + 1
LHS = RHS
Q-19) What is the area of the largest circular disc cut from a square of side $2/√π$ units?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Side of square = $2/√π$
radius of circular disc = $2/√π × 1/2 = 1/√π$
area of disc = $π r^2 = π (1/√π)^2$ = 1 unit 2
Q-20) A line segment AB is the diameter of a circle with centre at O having radius 6.5 cm. Point P is in the plane of the circle such that AP = x and BP = y. In which one of the following cases the point P does not lie on the circle ?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
![]()
P does not lie on the circle at x = 6.5cm and
y = 6.5 cm because, as <APB = 90°
then, $AB^2 ∼ ∼ = AP^2 ∼ ∼ + BP^2$
$(13)^2 ≠ (6.5)^2 ∼ ∼ + (6.5)^2$
Hence, point P does not lies on the circle ∼