Practice Mensuration - quantitative aptitude Online Quiz (set-1) For All Competitive Exams
Q-1) Using the data in the above question, what is the breadth of the rectangle ?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Breadth of the rectangle is 8 units, as solved above
Q-2) In the figure given below, PQ is parallel to RS and PR is parallel to QS. If ∠LPR = 35° and ∠ UST = 70°, then what is ∠MPQ equal to ?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
![]()
PQ || RS
PR|| QS
∴ PQRS is a || gm
∠LPR = 35° and ∠UST = 70°
∠UST = ∠RSQ (Vertically opposite)
∠RSQ = ∠RPQ (opposite angle of 11 gm)
∠LPR + ∠RPQ + ∠MPQ = 180°
35° + 70° + ∠MPQ = 180°
∠MPQ = 180 – 105
∠MPQ = 75°
Q-3) The diagonals of a trapezium are at right angles, and the slant sides, if produced, form an equilateral triangle with the greater of the two parallel sides. If the area of the trapezium is 16 square cm, then the distance between the parallel sides is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
![]()
ΔEAB is equilateral
ΔEDC is also equilateral
Area of trapezium ABCD
= $(1/2 × DB × OA) + 1/2 (DB × OC)$
= $1/2$ × DB × AC
Let AO = OB = x and DO = OC = y
Area (ABCD) = $1/2 (x + y)^2$ = 16(given)
⇒ x + y = 4 $√2$ ... (i)
ΔAOB is a right angled isosceles triangle.
So, AB = $√{x^2 + x^2} = √2x$
Similarly, DC = $√2$y
Now, FG = EF – EG
⇒ FG = AB sin 60° – DC sin 60°
= $√3/2 (AB - DC) = √6/2$ (x - y) ... (ii)
Area of trapezium
= Area ΔEAB – Area ΔEDC
= $√3/4 (AB^2 - DC^2)$
= $√3/4 [(x√2)^2 - (y√2)^2]$
⇒ Area = $√3/2$ (x + y) (x – y)
Now, $√3/2$ (x + y)(x - y) = 16
⇒ x – y = ${32}/{√3 (x + y)} ⇒ x - y = 8/√6 (∵ x + y = 4√2)$
Height = $√6/2 (x - y) = √6/2 × 8/√6$ = 4 cm
Q-4) Let LMNP be a parallelogram and NR be perpendicular to LP. If the area of the parallelogram is six times the area of ΔRNP and RP = 6 cm what is LR equal to?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
![]()
Area of parallelogram = 6 × Area of ΔNPR
∴ NR × PL= 6 × $1/2$ × NR × PR
⇒ PL = 3PR (here, PL = PR + RL)
⇒ PR + RL= 3PR
⇒ RL= 2PL = 2 × 6 = 12 cm
Q-5) 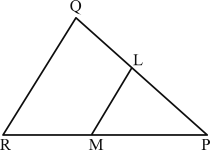
In the figure given above, LM is parallel to QR. If LM divides the ΔPQR such that area of trapezium LMRQ is two times the area of ΔPLM, then what is ${PL}/{PO}$ equal to?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
In the given figure.
ar MRQL = 2 ar ΔPLM
Let area of ΔPLM be x, then
∴ the area of trapezium = 2x
∴ ar ΔPQR = 2x + x = 3x
Here it is clear from the given figure that ΔPQR ∼ ΔPLM
![]()
∴ ${\text"ar ΔPQR"}/{\text"ar ΔPLM"} = {3x}/x$
${PL^2}/{PQ^2} = 1/3 ∴ = {PL}/{PQ} = 1/√3$
Q-6) The lengths of three line segments (in cm) are given in each of the four cases. Which one of the following cases is not suitable to be the three sides of a triangle?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
We know that, in any triangle the sum of two sides is always greater than its third side and the difference of two sides is always less than its third side.
Only option (c) is not satisfy the above conditions
(i) 2 + 3 ≯ 5 (ii) ∼ 5 – 2 ≮ 3
Q-7) In the figure given below, what is ∠BCD equal to?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
∠BAC = ∠BDC {Angle made by same chord BC in the same side}
Now, from ΔBCD, sum of angles = 180°
∠CBD + ∠BDC + ∠BCD = 180°
∴ ∠BCD = 180° – 100° = 80°
Q-8) In the figure given below, ABC is a triangle. BC is parallel to AE. If BC = AC, then what is the value of ∠CAE?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Given that, BC || AE
∠CBA + ∠EAB = 180°
⇒ ∠EAB =180° – 65° = 115°
∵ BC= AC
Hence, ΔABC is an isosceles triangle
![]()
∠CBA= ∠CAB = 65°
Now, ∠EAB = ∠EAC + ∠CAB
⇒ 115° = x + 65° ⇒ x = 50°
Q-9) 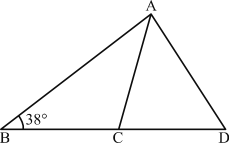 In the figure given, ∠B = 38°, AC = BC and AD = CD. What is ∠D equal to?
In the figure given, ∠B = 38°, AC = BC and AD = CD. What is ∠D equal to?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Given, AC = BC
![]()
In ΔABC, ∠ABC = ∠CAB
∠ABC = ∠CAB = 38° (∴ AC = BC)
∠ACB = 180° – (∠ABC + ∠CAB)
= 180° – (38° + 38°) = 180° – 76° = 104°
In ΔACD, ∠ACD = 180° – 104° = 76°
and ∠ACD = ∠CAD = 76°
(∵ CD = AD)
∴ ∠ADC = 180° – (∠ACD + ∠CAD)
= 180° – (76° + 76°) = 28°
Q-10) A rectangle carboard is 18 cm × 10 cm. From the four corners of the rectangle, quarter circles of radius 4 cm are cut. What is the perimeter (approximate) of the remaining portion?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
![]()
Remaining perimeter
= $({2 πr}/4)$4 + 10 + 2 + 10 + 2 = 2 × 3.14 × 4 + 24
= 25.12 + 24 = 49.12 cm
= 49.1 cm (approx)
Q-11) A cistern 6 m long and 4 m wide contains water up to a depth of 1 m 25 cm. The total area of the wet surface is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Area of the wet surface = [2(lb + bh + lh) – lb]
= 2(bh + lh) + lb
= [2(4 × 1.25 + 6 × 1.25) +6 × 4] $m^2 = 49 m^2$.
Q-12) ABCD is a quadrilateral with AB = 9 cm, BC = 40 cm, CD = 28 cm, DA = 15 cm and angle ABC is a right-angle.
What is the area of quadrilateral ABCD ?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
![]()
In right triangle ABC,
AC = $√{(AB)^2 + (BC)^2} = √{(40)^2 + (9)^2}$ = 41 cm
Area of ΔABC = $1/2 × 9 × 40 = 180 cm^2$
∵ Area of quadrilateral ABCD
= 126 + 180 = 306 $cm^2$
Q-13) Consider the following statements : Two triangles are said to be congruent, if - Three angles of one triangle are equal to the corresponding three angles of the other triangle.
- Three sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding three sides of the other triangle.
- Two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two sides and the included angle of the other triangle.
- Two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two angles and the included side of the other triangle.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Q-14) The cross section of a canal is a trapezium in shape. If the canal is 7 metres wide at the top and 9 metres at the bottom and the area of cross-section is 1280 square metres, find the height of the canal.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
![]()
Let the height of canal = h.
Then, area of canal = $1/2$ × h(9 + 7)
or = 1280 = $1/2$ h(16)
∴ h = ${1280 × 2}/{16}$ = 160m
Q-15) A tent is in the form of a right circular cylinder surmounted by a cone. The diameter of the cylinder is 24 m. The height of the cylindrical portion is 11 m, while the vertex of the cone is 16 m above the ground. What is the area of the curved surface for conical portion?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Slant height of the cone = $√{5^2 + 12^2}$
= $√{2 + 144} = √{169} = 13m$
![]()
Curved surface area for conical portion = πrl
= ${22}/7 × 12 × 13 = {3432}/7$sq m
Q-16) The curved surface area of a right circular cone is 1.76 $m^2$ and its base diameter is 140 cm. What is the height of the cone?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Radius of cone = ${140}/2 = 70 cm = {70}/{100}$ = 0.7m
Curved surface are = πrl = 1.76 $m^2$
${22}/7$ × 0.7 × l = 1.76
l = ${1.76 × 7}/{22 × 0.7}$ = 0.8m = 80 cm
height of cone = $√{l^2 - r^2} = √{80^2 - 70^2}$
= $√{1500} = 10√{15}$ cm
Q-17) In the figure given below, SPT is a tangent to the circle at P and O is the centre of the circle. If ∠QPT = α, then what is ∠POQ equal to?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Q-18) What is the area of an equilateral triangle having altitude equal to 2 $√3$ cm?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Area of equilateral triangle = $√3/4 a^2$
![]()
⇒ $1/2 × a × h = √3/4 a^2$
⇒ h = $√3/2 a^2$
⇒ 2$√3 = √3/2 a^2$
⇒ $a^2$ = 2 × 2 = 4
a = 2 cm
Area of equilateral triangle
= $√3/4 a^2$
= $√3/4 (a)^2 = √3/4 (2)^2$
= $√3 cm^2$
Q-19) The base of an isosceles triangle is 300 unit and each for its equal sides is 170 units. Then the area of the triangle is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Let ABC be an isosceles triangle.
![]()
Area = $1/2$ × AD × BC
= $1/2 × √{(170)^2 - (150)^2} × 300$
= $1/2 × √{28900 - 22500} × 300$
(∵ ΔADC is a right angled triangle then by pythagoras theorem, we find AD)
= 150 × $√{6400}$ = 150 × 80 = 12000 units.
∴ Option (a) is correct.
Q-20) a, b, c, b are non-zero integers such that (ab) divides (cd). If a and c are coprime, then which one of the following is correct?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Since we are given that a and c are co-prime i.e. HCF of a and c is 1, therefore we can say that a definitely divides d exactly.
So, a is a factor of d.